What can you do in Nuwa with Vector Maps?
Chenge Zang, Tersus GNSS 24 August, 2022
Vector data is the most common type of geographic data. Compared with raster data, which uses cell matrix to represent geographic data, vector data has better accuracy and display quality, which means no loss of accuracy and graphic distortion when scaling the vector maps. Generally, points, lines and polygons are used as vector data to represent geographic data. DXF, DWG, KML, KMZ, SHP, LandXML, etc, are commonly used vector data formats in the field of GIS.
We often get vector data files in some format such as DXF and LandXML. They may be the results of exports from third party software. They may be design files, and surveyors need to stake out the location of the features in the field based on the vector maps. They may be mapping files, and surveyors need to check in the field whether the mapping is correct, or collect new features to add to the map. So what can you do in Nuwa with these vector maps?
First, in [Export] - [Other Import], choose the correct vector file format. Two import types are provided, one is to read only the point data in vector files and import them into the target point list; the other is to import the vector data containing points and lines as a form of a base map as reference map, and draw the vector map directly in the Survey and Stakeout interface. At present, we already support vector base map in DXF, KML, KMZ and LandXML formats, and we will support more formats in the future.
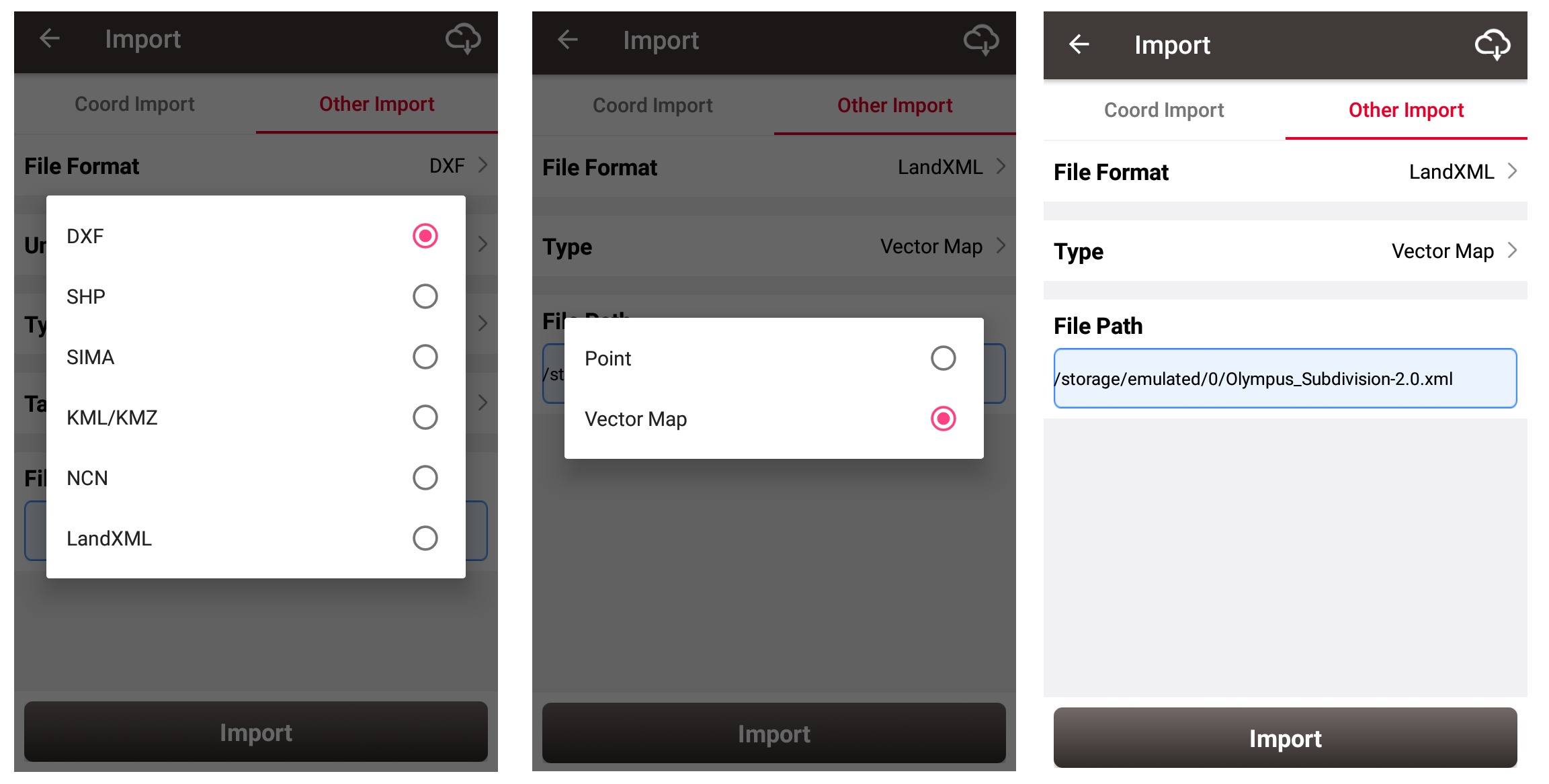
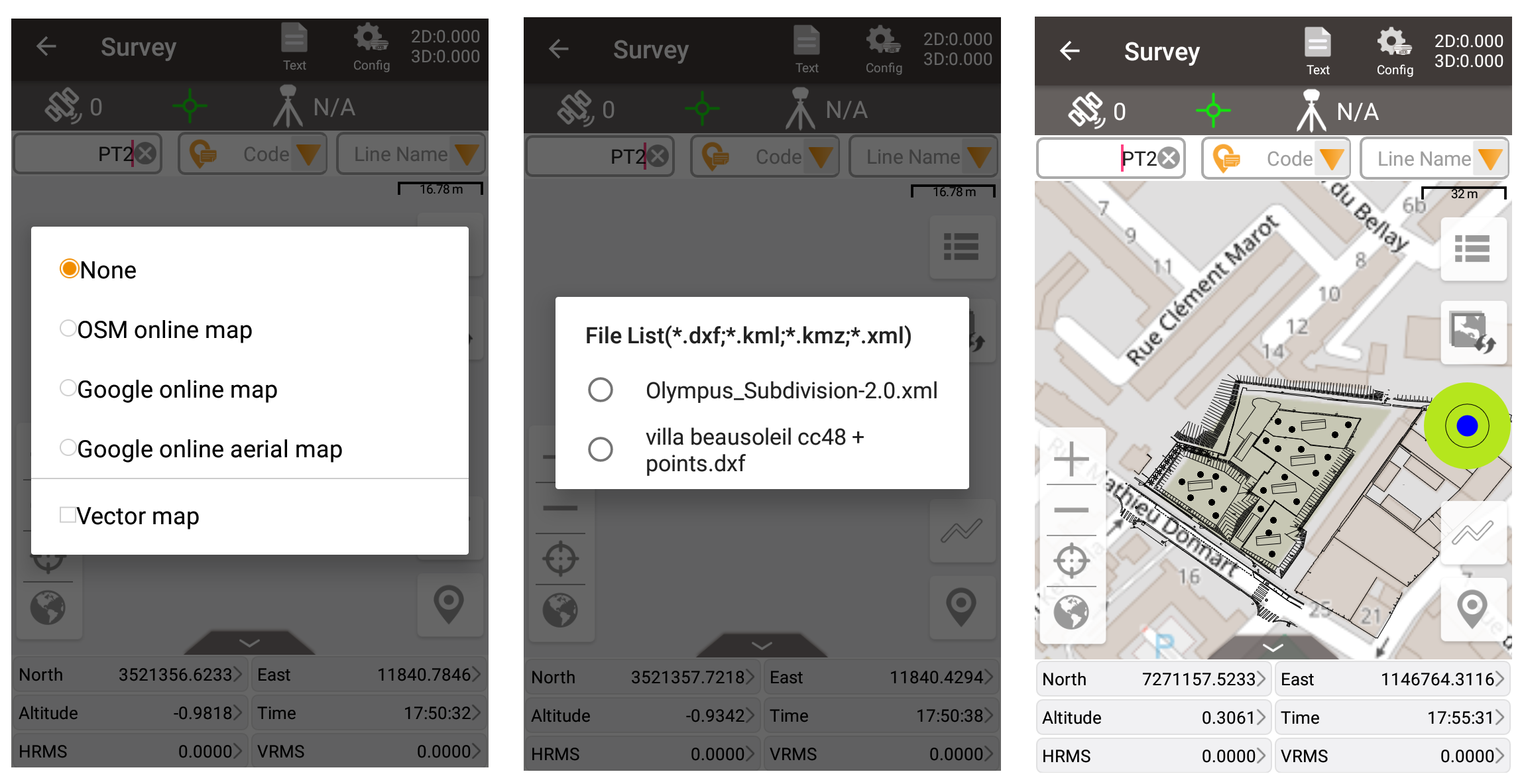
After finishing importing vector drawings as vector map, click the button in the Survey or Stakeout interface, click [vector map], and then check the imported vector map. You can see that the vector drawings has been displayed in the interface. Note that since the drawing of the vector data involves coordinate conversion, make sure the correct project coordinate system parameters are configured before the vector map imported, so that the vector drawings can be drawn in the correct position.
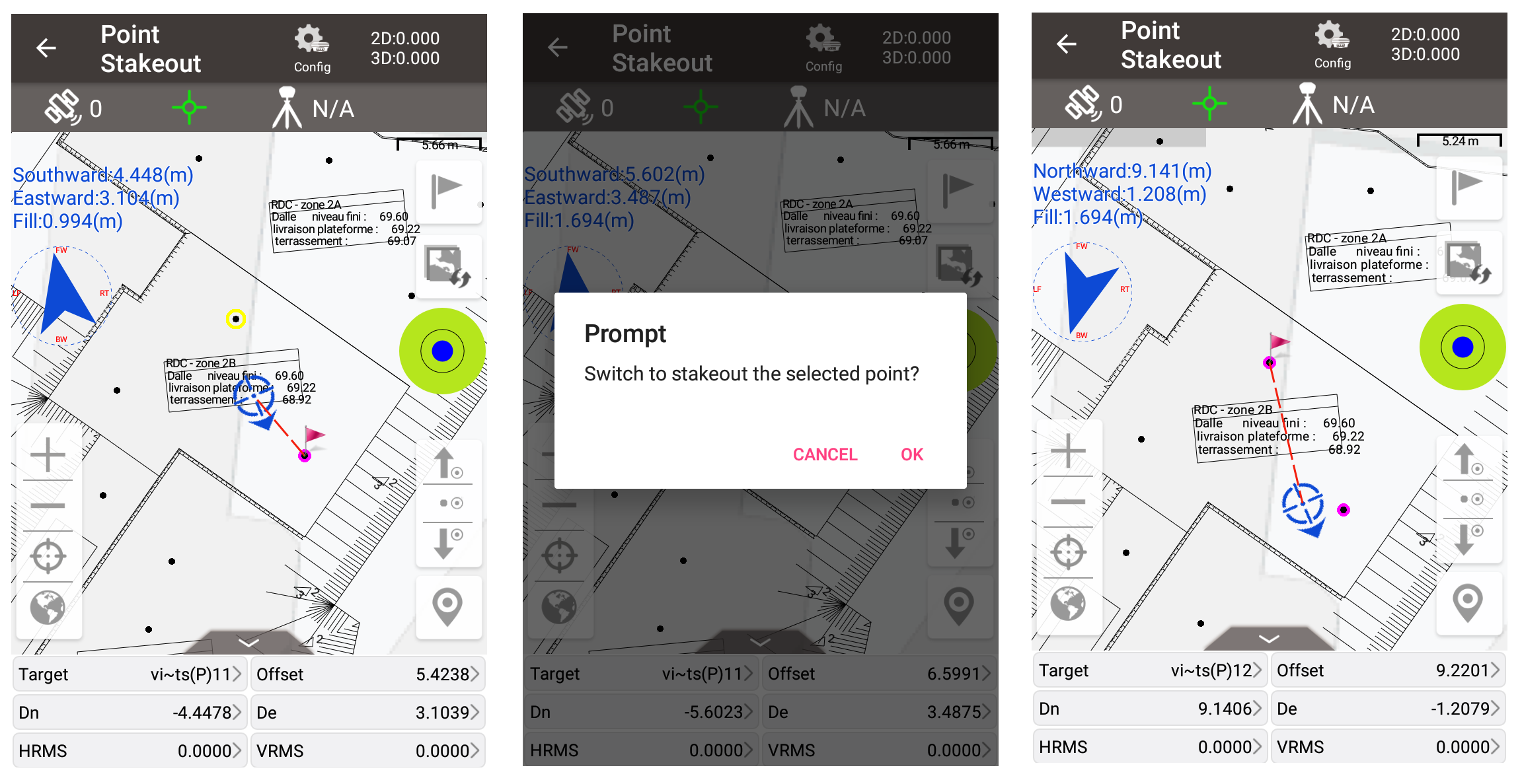
In the stakeout module, click on points on the vector maps to switch to stake the selected point directly. Click on polylines or arcs on the vector maps, to switch to stake points by interval, or stake to the nearest point on the line.
In addition, if you apply online map or online satellite map at the same time, both the vector map and online map will be overlapped and displayed in front of you at the same time, which is more intuitive. Together with the functions of rotating map when staking, the staking process will become more interesting!
For DXF and DWG files, we has developed another module based on CAD platform, where there are more professional CAD tools. For more information, please refer to the previous articles or feel free to contact us.
About Tersus GNSS Inc.
Tersus GNSS is a leading Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) solution provider. Our offerings and services aim to make centimeter-precision positioning affordable for large-scale deployment.
Founded in 2014, we have been pioneers in design and development GNSS RTK products to better cater to the industry’s needs. Our portfolios cover GNSS RTK & PPK OEM boards, David GNSS Receiver, Oscar GNSS Receiver, MatrixRTK [GNSS CORS Systems] and inertial navigation systems.
Designed for ease of use, our solutions support multi-GNSS and provide flexible interfaces for a variety of applications, such as UAVs, surveying, mapping, precision agriculture, lane-level navigation, construction engineering, and deformation monitoring.
Sales inquiry: sales@tersus-gnss.com
Technical support: support@tersus-gnss.com
