What is ITRF and ITRS?
Zoe Zhao, Tersus GNSS 25 Oct. 2023
Why are there people saying that "I am using WGS84 (ITRF96)"?
1. Definitions
The International Terrestrial Reference System (ITRS) describes procedures for creating reference frames suitable for use with measurements on or near the Earth's surface.
An International Terrestrial Reference Frame (ITRF) is a realization of the ITRS. Its origin is at the center of mass of the whole earth including the oceans and atmosphere. ITRF is a set of physical points with precisely determined coordinates in a specific coordinate system (cartesian, geographic, mapping...) attached to a Terrestrial Reference System. New ITRF solutions are produced every few years, using the latest mathematical and surveying techniques to attempt to realize the ITRS as precisely as possible.
2. What does the ITRF do?
ITRF is maintained by the International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS – http://www.iers.org), one of the many important IAG services, on the basis of globally coordinated, science-oriented infrastructure committed voluntarily by a large number of national agencies and research institutes. Most regional and global reference frames are today aligned or related to ITRF. Interoperability of georeferenced datasets and services depends on well-defined standards or special agreements for the determination and maintenance of the frames, and the availability of transformations between the different frames.
The ITRF, regional and national reference frames, can these days be very easily connected to using the signals from Global Satellite Navigation Systems (GNSS), such as GPS, to determine position with respect to such frames to sub-centimetre accuracy. However, in a hierarchical sense the ITRF is the fundamental frame, being the product of an international, collaborative geodetic enterprise that has been engaged in this task for several decades. All other frames are subordinate, and can (must) be aligned or connected to the ITRF using GNSS.
As of April 2022, IERS has released a total of 14 versions of the reference framework from ITRF88 to ITRF2020. Due to continuous improvements in data quality, analysis strategies, etc., the accuracy of each version is better than the past version.
Different ITRF frames can be transformed using similar coordinate system transformations. Typically, 14 conversion parameters are used for ITRF conversion which includes 7 conversion parameters and 7 conversion parameters rate. These 14 conversion parameters are obtained using the Bursa-Whorf seven parameters. To obtain conversion parameters and rates from ITRF2020 to previous frames, you can visit the website: https://itrf.ign.fr/en/solutions/transformations.
3. What is the relationship between ITRF and coordinate system?
The current GNSS systems/frames in existence are WGS84 for GPS, PZ-90 for GLONASS, CGCS2000 for COMPASS, GTRF for Galileo and JCS for QZSS. And these systems/frames are more or less connected to one another or are related to the ITRS/ITRF.
WGS84
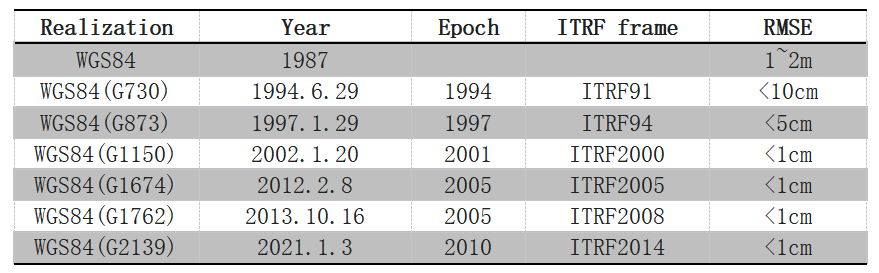
Since its inception in 1987, there have been six subsequent realizations of the World Geodetic System 1984 designated. The latest version is WGS84 (G2139), which was launched on January 3, 2021.
G represents the use of GPS measurements to obtain coordinates, and the number after G represents GPS week approved by NGA.
See the table below for detailed information on the establishment and update of the WGS84 coordinate system. It can be seen that after each update of the ITRF reference frame in recent years, WGS84 will release a corresponding version, and the accuracy level of both remains within ±1cm.
4. So how to determine the epoch and frame of conventional RTK and TAP services?
The epoch and frame of the Rover are determined by the Base station; the epoch and frame of the Base station are determined by the input known coordinates; if the base station does not input known coordinates, it is determined by the ephemeris; the ephemeris is divided into precision ephemeris and broadcast ephemeris.
The TAP service is the latest ITRF 2020 and the current epoch.
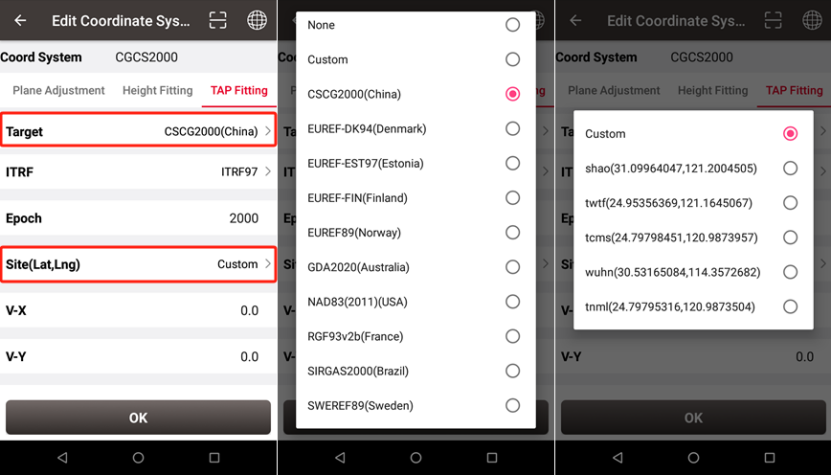
In the Nuwa software, there is an option in the coordinate system to calculate the TAP results to the frame and epoch corresponding to the specific coordinate system.
For example: Select "Target" as "CGCS2000", the ITRF frame and epoch corresponding to the CGCS2000 coordinate system will be automatically displayed, and then select a site from the "Site" list to achieve frame and epoch conversion (the site list displays the closest to the current location 5 sites).
About Tersus GNSS Inc.
Tersus GNSS is a leading Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) solution provider. Our offerings and services aim to make centimeter-precision positioning affordable for large-scale deployment.
Founded in 2014, we have been pioneers in design and development GNSS RTK products to better cater to the industry’s needs. Our portfolios cover GNSS RTK & PPK OEM boards, David GNSS Receiver, Oscar GNSS Receiver, MatrixRTK [GNSS CORS Systems] and inertial navigation systems.
Designed for ease of use, our solutions support multi-GNSS and provide flexible interfaces for a variety of applications, such as UAVs, surveying, mapping, precision agriculture, lane-level navigation, construction engineering, and deformation monitoring.
Sales inquiry: sales@tersus-gnss.com
Technical support: support@tersus-gnss.com
